The electric radiant tubes that we make can be used for vertical or horizontal operation. We can create tailored parts required for your specific projects. Our heating tubes can operate at temperatures up to:
- 1100 °C for heat-resistant steel tubes
- 1300 °C for silicon carbide (SiC) tubes
Installed capacities can be of up to 30 kW / linear metre of tube, depending on diameter and temperature.
Glow plugs are heating elements that can be easily removed from the furnace from outside. This is a true advantage for furnaces that are required to operate continuously, or under atmosphere. In these cases, the heating elements can be replaced without having to shut down the facility.
Thanks to our know-how, we are able to create high-quality hot glow plugs while optimising costs.
Do not hesitate to contact us for your stock or for new equipment, installation, repair or servicing.
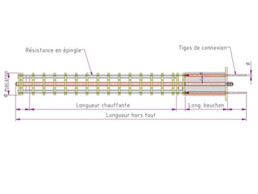
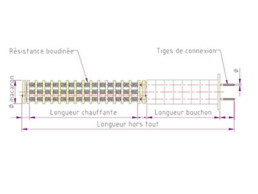
Heating glow plug examples. Birdcage glow plug and spiral glow plug
Hot glow plugs with metal resistances
Resistances are made from resistive nickel-chromium (NiCr) or iron-chromium-aluminium (FeCrAl) wire.
The heating component consists of a series of coils or hairpins connected by bridges.
The term BIRDCAGE refers to a glow plug with hairpin configuration.
In addition to the resistance, a glow plug comprises:
- An insulating cap with end plate
- “cold” connecting rods
- ceramic spacer support stools and tubes
We also propose metal resistances alone.
Our sales team is also available to provide you with any explanations you may require and to give you our prices.
Heating glow plugs with silicon carbide (SiC) resistances
For some applications, requiring higher field densities or temperatures, we offer glow plugs fitted with silicon carbide (SiC) resistances.
These glow plugs can be used in radiant tubes.
Examples of heating glow plugs with silicon carbide resistance
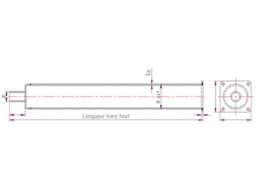
Radiant tubes
Radiant tubes are made from heat-resistant steel or silicon carbide (SiC).
In the case of heat-resistant steel tubes, the grade used and thickness are determined by
- the application: furnace temperature and atmosphere. . .
- the manufacturing process: rolled and welded or centrifuged
SiC tubes are used for higher temperature applications, with greater field densities, though their mechanical fragility must be taken into consideration.